Autosomal Recessive Trait Punnett Square Calculator
Understanding how recessive traits are inherited is essential for students, educators, and genetics enthusiasts. Our Autosomal Recessive Trait Punnett Square Calculator helps you easily visualize inheritance patterns when both parents carry a recessive allele (a). Discover more genetic tools and resources on our main website.
How This Calculator Works
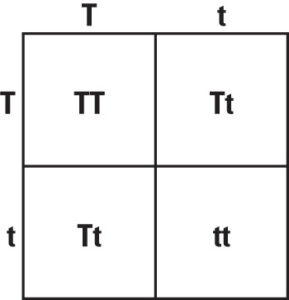
Select the genotypes of Parent 1 and Parent 2 (AA = homozygous dominant, Aa = heterozygous carrier, aa = homozygous recessive). Click Calculate to generate a 2×2 Punnett square that shows all possible offspring genotypes and their probabilities.
What You'll See
- Genotypes: AA, Aa, or aa with their percentage frequencies.
- Phenotypes: Recessive traits appear only in aa offspring, while AA and Aa appear phenotypically dominant.
- Carrier Probability: Understand the likelihood of producing carriers (Aa) or affected offspring (aa).
Why It Matters
Autosomal recessive inheritance means that two copies of the recessive allele (aa) are necessary to express the trait. This calculator helps:
- Students practice genetics problems with real-time examples.
- Educators demonstrate the probabilities of carrier and affected offspring.
- Families understand the risk of transmitting autosomal recessive conditions like cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia.
You can also go through – Autosomal Dominant Trait Punnett Square Calculator
Usage Example: Aa × Aa
- Genotypic ratio: 25% AA, 50% Aa, 25% aa
- Phenotypic ratio: 75% show the dominant trait (AA or Aa), 25% express the recessive trait (aa).
This calculator presents these results visually in a Punnett square, making complex genetics easy to understand.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Select parental genotypes from the dropdown menus.
- Click Calculate to generate the Punnett square.
- View the results: genotype percentages and phenotype outcomes.
- Download or copy results for reports or classwork.
Key Genetic Concepts
- Homozygous vs. Heterozygous
Homozygous (AA or aa) means both alleles are the same; heterozygous (Aa) means they differ. - Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
Two recessive alleles (aa) are needed for the trait to appear. Carriers (Aa) do not show the trait but can pass it to their children. - Mendel’s Laws
Each parent passes one allele to each offspring, making each outcome equally probable in the Punnett square.
Conclusion
Our Autosomal Recessive Trait Punnett Square Calculator makes genetics easier to understand, visualize, and share. Whether you’re studying Mendelian genetics or exploring hereditary diseases, this tool provides a clear picture of recessive trait inheritance—helping students, teachers, and curious minds alike.
